Diseases of the Mind
Amnesia

A disturbance in the memory of information stored in long-term memory, in contrast to short-term memory, manifested by total or partial inability to recall past experiences. Amnesia has two main causes organic or functional. Organic causes include specific drugs or degenerative diseases that impairs your memory in remembering certain things and events. Functional causes are mainly psychological as in defense mechanisms of the brain to forget traumatic incidents. click here for more information on amnesia
Dementia - the deterioration of your cognition which targets different areas of brain: communication, memory, orientation, problem solving and attention. It is not a specific disease but a group of symptoms that has more than 60 causes including stroke, Parkinson's disease, or AIDS/HIV.
Types of Dementia:
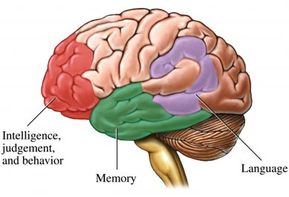
- Cortical Dementia - The cerebral cortex is affected. This is the outer layer of the brain. The cerebral cortex is vital for cognitive processes, such as language and memory. Alzheimer's disease is a form of cortical dementia, as is CJD (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease).
- Subcortical Dementia - A part of the brain beneath the cortex (deeper inside) becomes affected or damaged. Language and memory are not usually affected. A patient with subcortical dementia will usually experience changes in his personality, his thinking may slow down, and his attention span may be shortened. Dementias which sometimes result from Parkinson's disease are subcortical dementias, as are those caused by AIDS and Huntington's disease.
Alzheimer's Disease:
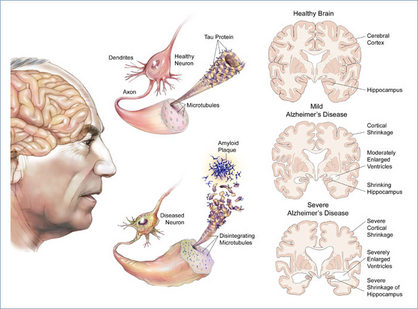
The most known cause of dementia which usually brings along memory impairment, language problems, decision and judgment ability, and personality impairment. Alzheimer's disease is characterized by two abnormalities in the brain: amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Amyloid plaques are clumps of protein with neurons and other cells. The protein called Tau twists into pairs and becomes tangled, disintegrating microtubules, and blocking the transport of neuron communication.
The most known cause of dementia which usually brings along memory impairment, language problems, decision and judgment ability, and personality impairment. Alzheimer's disease is characterized by two abnormalities in the brain: amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Amyloid plaques are clumps of protein with neurons and other cells. The protein called Tau twists into pairs and becomes tangled, disintegrating microtubules, and blocking the transport of neuron communication.
The problem with Dementia and Alzheimer's disease is that it effects the family members as well as the diseased person. If your loved ones don't remember who you are it mentally effects the family. The people that have AD are often found to respond to music and pictures. People with Dementia also either remember their childhood, but get the details messed up. The more involved the patients is, however, in daily life and activities the more able they are to recall memories. Some times there will be fleeting moments where these patients do remember, if only for a second. Speaking in terms of identity, AD hurts a person's identity because it wipes out the memories of their life, and since memories define us, there identities are for the most part loss.
Stroke:
The destruction of both hippocampus has disastrous effects on long-term memory, preventing the individual from learning anything new whatsoever. The most important evidence of the role of the hippocampus in transferring long-term memories has been provided by subjects who had sustained damage to both hippocampus and could not keep things in their memories for more than a few moments.
The destruction of both hippocampus has disastrous effects on long-term memory, preventing the individual from learning anything new whatsoever. The most important evidence of the role of the hippocampus in transferring long-term memories has been provided by subjects who had sustained damage to both hippocampus and could not keep things in their memories for more than a few moments.
http://www.seniorhomecareinformation.com/dementia/dementia-and-alzheimers-support-products-now-available-on/